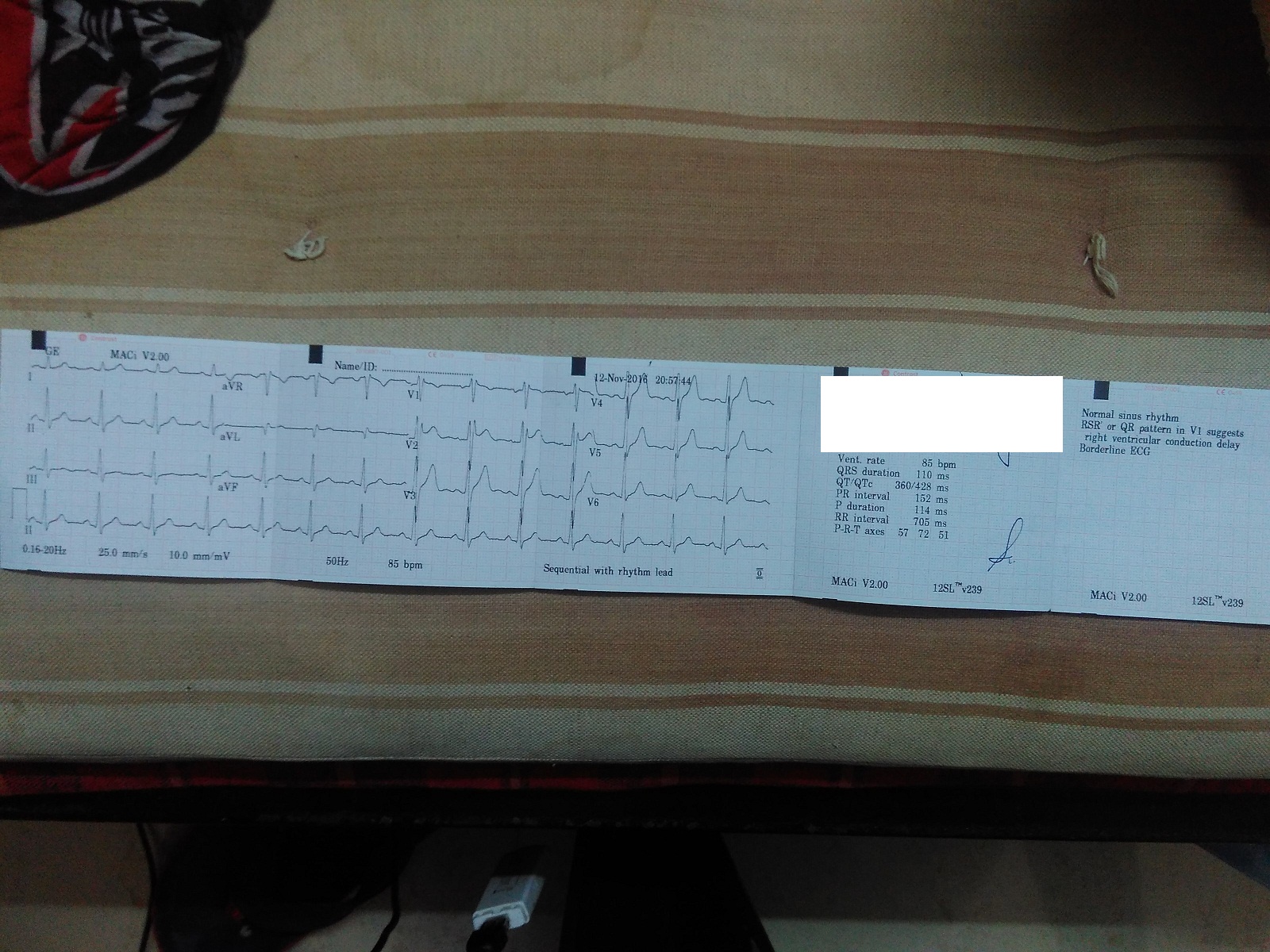
Borderline ECG readings can often raise concerns for individuals and healthcare providers alike. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a critical diagnostic tool used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. When an ECG result is labeled as "borderline," it indicates that certain aspects of the reading fall outside the normal range, but not enough to be classified as abnormal. Understanding what this means is essential for both patients and medical professionals.
In today's fast-paced world, heart health is a growing concern. Early detection and accurate interpretation of ECG results are crucial for preventing serious cardiovascular issues. A borderline ECG may indicate underlying conditions that require further investigation, making it vital to comprehend its implications fully.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the meaning of borderline ECG, its potential causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures. We will also explore how lifestyle changes and medical interventions can help manage the risks associated with borderline ECG results, ensuring you have all the information you need to make informed decisions about your health.
Read also:Kunal Yadav Ias The Inspiring Journey Of A Dedicated Civil Servant
Table of Contents
- What is Borderline ECG?
- How Does an ECG Work?
- Common Interpretations of Borderline ECG
- Causes of Borderline ECG
- Symptoms Associated with Borderline ECG
- The Diagnosis Process
- Risk Factors for Borderline ECG
- Management Options for Borderline ECG
- Lifestyle Changes to Improve Heart Health
- Conclusion
What is Borderline ECG?
A borderline ECG refers to an electrocardiogram reading that falls between normal and abnormal. This classification means that certain parameters, such as heart rate, rhythm, or electrical patterns, are slightly outside the standard range but do not meet the criteria for a definitive diagnosis of heart disease or other cardiac conditions.
Borderline ECG results can be confusing for patients, as they often require further evaluation to determine their significance. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can interpret the findings in the context of your overall health and medical history.
Normal vs. Borderline ECG Readings
- Normal ECG: Shows regular heartbeats, normal intervals, and no signs of arrhythmia or ischemia.
- Borderline ECG: Exhibits minor deviations from normal values, such as slightly prolonged intervals or mild ST-segment changes.
- Abnormal ECG: Indicates significant abnormalities that may suggest heart disease or other serious conditions.
How Does an ECG Work?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Electrodes are placed on the skin, and they detect the electrical impulses generated by the heart as it beats. These signals are then translated into a graph that displays the timing and strength of each heartbeat.
The ECG provides valuable information about the heart's rhythm, rate, and electrical conduction. By analyzing the patterns on the graph, healthcare providers can identify potential issues such as arrhythmias, ischemia, or structural abnormalities.
Key Components of an ECG
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization.
- QRS Complex: Indicates ventricular depolarization.
- T Wave: Reflects ventricular repolarization.
- PR Interval: Measures the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization.
- QT Interval: Represents the duration of ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
Common Interpretations of Borderline ECG
Borderline ECG results can vary depending on the specific deviations observed. Some common interpretations include:
- Mild ST-Segment Changes: Suggestive of early ischemia or electrolyte imbalances.
- Prolonged QT Interval: May indicate an increased risk of arrhythmias.
- Borderline Heart Rate: Slightly elevated or reduced heart rate without clinical significance.
- Minor Arrhythmias: Occasional premature beats or irregularities that do not affect overall heart function.
These findings may or may not be clinically significant, depending on the patient's symptoms and medical history. Further testing and monitoring are often necessary to clarify the implications of borderline ECG results.
Read also:Josh Richards The Rise Of A Digital Age Sensation
Causes of Borderline ECG
Several factors can contribute to borderline ECG readings. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for determining the appropriate course of action. Some common causes include:
- Age and Gender: Normal ECG patterns can vary based on age and gender, leading to borderline results in certain populations.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Abnormal levels of potassium, calcium, or magnesium can affect heart electrical activity.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as antiarrhythmics or antidepressants, may alter ECG readings.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can temporarily affect heart rate and rhythm, resulting in borderline ECG findings.
In some cases, borderline ECG results may be benign and require no further intervention. However, in other instances, they may indicate the presence of an underlying condition that warrants further investigation.
Medications That Can Affect ECG Readings
- Beta-Blockers: May cause bradycardia or prolonged PR intervals.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Can lead to slower heart rates and altered electrical conduction.
- Antiarrhythmics: Designed to treat arrhythmias but may cause changes in ECG patterns.
Symptoms Associated with Borderline ECG
While borderline ECG results may not always be accompanied by noticeable symptoms, some individuals may experience mild symptoms that warrant attention. Common symptoms include:
- Palpitations: Feeling of irregular or rapid heartbeats.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: May occur due to changes in heart rate or rhythm.
- Shortness of Breath: Could indicate underlying cardiac or respiratory issues.
- Chest Discomfort: Mild chest pain or pressure that may be related to ischemia.
It is important to report any symptoms to your healthcare provider, even if they seem minor, as they may provide additional clues about the significance of borderline ECG findings.
The Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing the cause of borderline ECG results typically involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and additional diagnostic tests. Some common diagnostic procedures include:
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound waves to visualize the structure and function of the heart.
- Stress Test: Monitors heart activity during exercise to detect ischemia or arrhythmias.
- Holter Monitor: Provides a continuous recording of heart activity over 24-48 hours.
- Blood Tests: Evaluates electrolyte levels, cardiac enzymes, and other markers of heart health.
These tests help healthcare providers determine whether borderline ECG findings are benign or indicative of a more serious condition.
The Importance of Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring borderline ECG results and assessing any changes over time. Your healthcare provider may recommend periodic ECGs or other tests to ensure your heart health remains stable.
Risk Factors for Borderline ECG
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing borderline ECG findings. These include:
- Family History of Heart Disease: Genetic predisposition to cardiovascular conditions.
- Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure can affect heart structure and function.
- Diabetes: Increases the risk of developing ischemic heart disease.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and affects heart health.
Identifying and managing these risk factors can help reduce the chances of borderline ECG progressing to more serious conditions.
Preventing Cardiovascular Issues
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly lower the risk of developing borderline ECG findings and related conditions. Key strategies include maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco use, and managing stress effectively.
Management Options for Borderline ECG
The management of borderline ECG findings depends on the underlying cause and associated symptoms. In some cases, no specific treatment is required, while in others, lifestyle modifications or medical interventions may be necessary. Options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking.
- Medications: Prescribing medications to address underlying conditions such as hypertension or arrhythmias.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up and periodic ECGs to track changes over time.
Working closely with your healthcare provider is essential for developing an effective management plan tailored to your individual needs.
Emerging Treatments and Technologies
Advancements in medical technology continue to improve the accuracy and interpretation of ECG results. Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems offer new opportunities for tracking heart health and detecting potential issues early.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Heart Health
Implementing positive lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on heart health and reduce the risk of borderline ECG findings. Key strategies include:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoiding Smoking: Quitting tobacco use is one of the most effective ways to improve heart health.
By adopting these habits, you can enhance your overall cardiovascular well-being and minimize the risk of developing borderline ECG findings.
Conclusion
Borderline ECG results can be concerning, but they often do not indicate serious underlying conditions. Understanding the meaning and implications of borderline ECG findings is essential for making informed decisions about your health. By working closely with your healthcare provider and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can effectively manage any associated risks and maintain optimal cardiovascular health.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information and to leave a comment below if you have any questions or feedback. Remember, early detection and prevention are key to maintaining a healthy heart. Explore our other articles for more insights into heart health and wellness.